NASA Compression After Impact Test Fixture
Model No. WTF-CN (Stainless Steel)
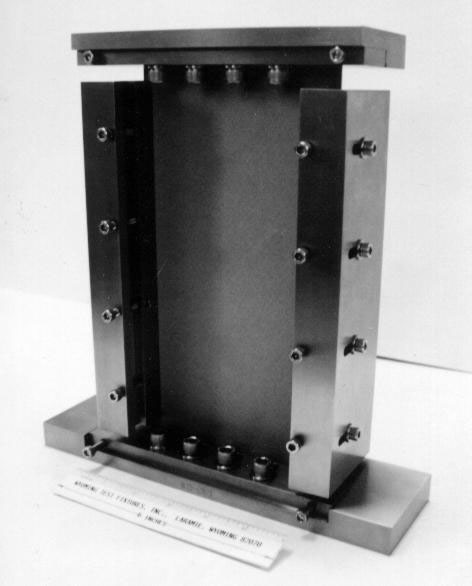
Fig. 1: Assembled fixture with specimen installed.
This version of the NASA Compression After Impact (CAI) Compression Test Fixture is an alternative to the more popular Boeing Compression After Impact Compression Test Fixture, Wyoming Test Fixtures, Inc. Model WTF-CI, described in Section C-3 in this website. Another NASA version, more closely resembling the Boeing fixture, is also available. Both NASA fixtures are described in detail in Reference 1, both utilizing a specimen 10" long and 5" wide, i. e., 4" longer and 1" wider than the Boeing specimen. Hence, more than twice as much material is required per specimen. Thus, the NASA versions have become much less commonly used. As in the Boeing method, a quasi-isotropic laminate is typically tested. The NASA fixture version shown here in Fig. 1 consists of four separate assemblies, each clamping onto an edge of the specimen as shown in the photograph. These assemblies stabilize the specimen against buckling. The lower assembly rests on the base the testing machine, and the compressive loading is applied to the test specimen through the top assembly using a flat compression platen in the cross head of the testing machine. Before being compression tested to failure, the specimen is subjected to an impact loading, typically using a drop-weight impact testing device, just as in the Boeing test method, which is described in Reference 2.
Sources of Additional Information:
1) NASA Reference Publication 1092, "Standard Tests for Toughened
Resin Composites ;" NASA-Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia,
Revised Edition, July 1983.
2) Boeing Specification Support Standard BSS 7260, "Advanced Composite
Compression Tests," The Boeing Company, Seattle, Washington, 1988.

